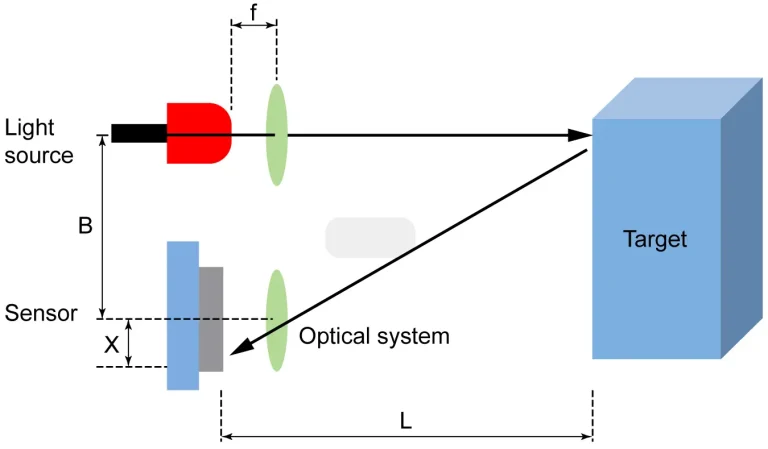
Understanding How Distance Sensors Work
Distance sensors are fascinating devices that measure the space between objects. They are essential in many fields, from robotics to automotive industries.
Understanding how these sensors work can be complex. But breaking it down into simple terms makes it easier.
There are various types of distance sensors, each with unique features. Ultrasonic, infrared, and laser sensors are among the most common.
Each type uses different methods to measure distance. For example, ultrasonic sensors use sound waves, while infrared sensors rely on light.
The choice of sensor depends on the application. Factors like accuracy, range, and environment play a crucial role.
Sensor technology has advanced significantly. Modern sensors are now more accurate and versatile.
They are integral to automation and smart systems. This makes them indispensable in today’s technology-driven world.
Understanding sensors is key to innovation. It opens doors to new possibilities in engineering and technology.
Summary
Distance sensors measure how far objects are using sound, light, or electromagnetic fields, with common types including ultrasonic, infrared, laser (LIDAR), capacitive, inductive, and radar. They rely on methods like time-of-flight, triangulation, and echo detection, and their performance hinges on range, accuracy, resolution, environment, and good installation/calibration. Selecting the right sensor balances application needs, conditions, and cost, supporting uses from automotive and robotics to healthcare and industrial automation. Ongoing advances—AI integration, better materials, and miniaturization—are making sensors more precise, versatile, and accessible.
What Are Distance Sensors?
Distance sensors are devices designed to measure the gap between themselves and nearby objects. They translate physical distance into electrical signals. This makes them useful in various applications, from industrial automation to home electronics.
These sensors come in many forms. They use different measurement techniques based on the type. Here’s a simple list of some common types:
- Ultrasonic sensors
- Infrared (IR) sensors
- Laser sensors (LIDAR)
- Capacitive and inductive sensors
- Radar sensors
These sensors are compact and precise. They enable machines to interact with their surroundings intelligently. Industries rely on them for tasks requiring precision like packaging and robotic navigation.
Distance sensors vary in complexity and cost. Choosing the right sensor depends on the specific needs of the task. Understanding the basics of how they work can help in selecting the appropriate sensor for any given application.
The Science Behind Distance Sensing: Key Principles
Distance sensors rely on fundamental scientific principles to function. These principles can include sound waves, light reflection, and changes in electric fields. Each principle offers unique advantages that suit different types of sensors.
Sound waves are a primary mechanism in ultrasonic sensors. These sensors emit sound waves that bounce off objects. The time it takes for the echo to return helps calculate the distance. This method works well in clear environments and over longer distances.
Light reflection forms the basis of infrared and laser sensors. These sensors project light, which reflects off surfaces. Measuring the time or angle of reflection helps determine the distance to the object. This method is highly accurate, often used in precise applications.
Other principles include:
- Capacitance changes
- Radar frequency shifts
- Magnetic field variations
Capacitive and inductive sensors detect distance by measuring changes in an electric field or a magnetic field. Each principle suits different environments, offering versatility. Understanding these principles aids in selecting the right sensor for any unique requirement.
Main Types of Distance Sensors
Distance sensors come in various types, each suited for specific applications. The most common types are ultrasonic, infrared, laser, capacitive, and inductive sensors. Each type uses different principles to measure distance.
Here’s a quick overview of these types:
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Use sound waves.
- Infrared Sensors: Rely on infrared light.
- Laser Sensors (LIDAR): Utilize laser beams.
- Capacitive Sensors: Detect changes in capacitance.
- Inductive Sensors: Use magnetic fields.
Ultrasonic Distance Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to measure distance. These sensors emit high-frequency sound waves, inaudible to human ears. When these waves hit an object, they bounce back to the sensor.
The time taken for the echo to return indicates the distance. Ultrasonic sensors are reliable in various environments but can struggle with soft or uneven surfaces.
Common applications for ultrasonic sensors include:
- Parking assistance in cars
- Robotic obstacle detection
- Liquid level measurement
These sensors are popular in robotics and automotive industries. Their ability to work under poor lighting conditions makes them highly versatile.
Infrared (IR) Distance Sensors
Infrared sensors measure distance using infrared light. They emit an IR beam toward an object. The sensor then measures the reflection angle or time to calculate distance.
These sensors excel in detecting heat variations. IR sensors are compact and provide quick response times. However, they can be affected by ambient light and reflective surfaces.
Typical applications include:
- Remote controls
- Motion detection in security systems
- Night vision equipment

Infrared sensors find wide use in consumer electronics. They are crucial in household appliances and smart home devices.
Laser Distance Sensors (LIDAR)
Laser sensors, known as LIDAR, use laser beams for distance measurement. They are highly accurate, providing precise readings over large distances. LIDAR emits laser pulses and measures the time taken for them to return.
These sensors are perfect for detailed mapping and surveying. They can distinguish small changes in distance, even in complex environments.
Common applications include:
- Autonomous vehicles
- Topographical mapping
- Industrial automation

LIDAR is essential in modern technologies like self-driving cars. Its high precision and long range make it indispensable in many fields.
Capacitive and Inductive Distance Sensors
Capacitive sensors detect changes in capacitance between the sensor and the object. They work best for objects within a close range and are sensitive to the dielectric properties of the material.
Inductive sensors, on the other hand, use magnetic fields. They are effective in detecting metallic objects. These sensors are less affected by environmental conditions.
Applications of these sensors include:
- Touch screens
- Metal detection in machinery
- Proximity sensing in automation
Capacitive and inductive sensors are valuable in manufacturing and consumer electronics. Their ability to measure small distances accurately makes them highly effective.
Radar and Other Advanced Distance Sensors
Radar sensors use radio waves to measure distance. They are highly effective over long ranges and in adverse weather conditions. These sensors are crucial in aviation and maritime applications.
Other advanced sensors include:
- Ultrawideband (UWB) sensors
- 3D range imaging sensors

Radar sensors provide robust performance where other sensors might struggle. They are vital in sectors like aerospace and defense. These advanced sensors keep evolving, offering enhanced performance for specialized applications.
Distance Sensing Methods Explained
Distance sensing methods vary greatly depending on the type of sensor used. Each method employs unique techniques to achieve accurate measurements. These methods are the backbone of sensor functionality.
Common distance sensing methods include:
- Time-of-Flight (ToF): Measures the time light or sound takes to travel to an object and back. Used in LIDAR and ultrasonic sensors.
- Triangulation: Utilizes angles and geometry to calculate distance. Often found in laser and IR sensors.
- Echo Detection: Relies on sound waves and their reflection times. Primarily used in ultrasonic sensors.
Different methods offer distinct advantages and are chosen based on application needs. For example, ToF provides high accuracy and is ideal for precision tasks.
Environmental factors and required accuracy levels greatly influence method selection. Users must consider the advantages and constraints of each method.
by Meskernel (How Does TOF Sensor Work? A Complete Engineer-Level Explanation)
Understanding these methods helps in selecting the right sensor for specific applications. The choice of method can impact sensor effectiveness in various scenarios.
Key Factors Affecting Sensor Performance
The performance of distance sensors is influenced by several key factors. Understanding these factors can aid in optimizing sensor usage for specific tasks.
Important factors include:
- Environmental Conditions: Temperature, humidity, and lighting can affect sensor accuracy and reliability.
- Calibration: Ensures the sensor provides correct measurements. Regular calibration is crucial.
- Power Supply and Stability: A stable power source is necessary for consistent performance.
Each factor plays a significant role in sensor effectiveness. For instance, environmental conditions can introduce errors in measurement.
Choosing sensors with the right specifications can minimize these issues. Proper maintenance and calibration ensure longevity and accuracy. Adjusting for these factors enhances sensor performance across varied applications.
Sensor Range, Accuracy, and Resolution
Sensor range, accuracy, and resolution are crucial specifications for evaluating sensor performance. Each determines how well a sensor can perform in its intended role.
- Range: Defines the maximum and minimum distance a sensor can measure.
- Accuracy: Indicates how closely the sensor’s measurement aligns with the actual distance.
- Resolution: Refers to the smallest discernible change in distance that the sensor can detect.
The choice of sensor depends on these factors. High accuracy and resolution are often needed for precision tasks. Conversely, a broad range is crucial for applications requiring long-distance measurements. Selecting the appropriate balance of these factors ensures optimal sensor functionality in diverse situations.
Choosing the Right Distance Measurement Tool
Selecting an appropriate distance measurement tool requires careful consideration of various factors. First, identify the specific requirements of your application. This includes the measurement range, accuracy needs, and environmental conditions in which the sensor will operate.
- Accuracy Needs: Determine the precision necessary for your application.
- Environmental Factors: Consider humidity, temperature, and light conditions.
- Cost: Balance your budget with performance demands.

by Meskernel (Laser Measurement Tool)
Budget constraints also play a significant role. Cost-effective solutions may suffice for less demanding tasks, while high-performance tasks might require more investment. Analyze these aspects thoroughly to ensure the chosen sensor meets your application needs efficiently. This approach helps in optimizing both performance and cost-effectiveness in your project’s sensor selection process.
Applications of Distance Measurement Sensors
Distance measurement sensors play critical roles across numerous industries, enhancing efficiency and safety. In the automotive sector, they are essential for applications like collision avoidance systems. Such systems help in detecting obstacles and maintaining safe distances, contributing to driver assistance technologies.
These sensors are also pivotal in robotics, where they facilitate precise navigation and object detection. Robotic systems utilize distance sensors for mapping environments and executing tasks with accuracy. This capability improves automation and intelligent functionality in manufacturing and service robots.
- Automotive: Collision avoidance, parking assist
- Robotics: Navigation, object detection
- Healthcare: Patient monitoring, diagnostics
In healthcare, distance sensors contribute to patient monitoring systems and diagnostics. They aid in non-invasive measurements, ensuring patient comfort and safety. The versatility of distance sensors positions them as indispensable tools in modern technology across various domains, driving advancements and innovative solutions.
Installation, Calibration, and Troubleshooting Tips
Proper installation is crucial for the optimal performance of distance sensors. Ensure sensors are mounted securely and oriented correctly to avoid inaccurate readings. Calibration is another vital step; it aligns the sensor’s output with real-world measurements.
- Install Securely: Prevent misalignment and vibrations.
- Calibrate Regularly: Ensure accuracy over time.
- Troubleshoot Issues: Check connections and reset configurations.
When troubleshooting, start by checking connections and power supplies. Look for physical obstructions that might affect sensor readings. If issues persist, consult the sensor’s manual for configuration resets and firmware updates. Remember, periodic maintenance can extend sensor life and reliability.

The Future of Distance Sensor Technology
The future of distance sensor technology is promising and full of innovation. Advances in materials and signal processing will enhance sensor capabilities. Additionally, miniaturization and cost reduction continue to drive accessibility.
Innovations like AI integration will further improve sensor performance and applications. We can anticipate smarter sensors that adapt to diverse environments with greater precision.
- AI Enhancement: Adaptive learning capabilities.
- Material Advances: Improved sensor durability.
- Miniaturization: Smaller, more affordable devices.
These developments will broaden sensor applications across industries. From autonomous vehicles to smart cities, the impact will be significant. As technology evolves, distance sensors will become more integral to our daily lives, offering smarter and more efficient solutions.
Conclusion: Understanding Sensors for Innovation
Understanding how distance sensors work is fundamental for technological innovation. These tools are vital across various industries, enhancing efficiency and safety in many applications.
The role of distance sensors in future developments is undeniable. As technology advances, the potential for more sophisticated, accurate, and versatile sensors will grow. By grasping how these sensors operate, we prepare for the challenges and opportunities they will present. Innovators and engineers can utilize this knowledge to create cutting-edge solutions that push boundaries, improve lives, and drive the future of smart technologies.